Will Robots Eliminate Many Humans From the Workplace?
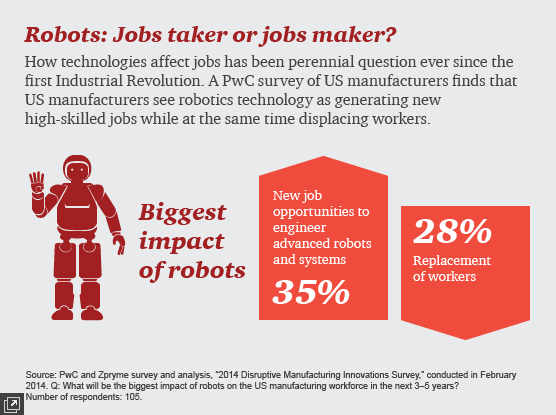
Robots have not eliminated work, but they have somewhat changed the types of jobs that humans do.
The spectre of robots taking over many of the world's jobs -- from retail to manufacturing to janitorial work to the military -- has been hanging over humanity for decades. The threat has expanded recently to include not just robots but also artificial intelligence -- algorithms -- with solutions like Google's search engine and IBM Watson proving that not only can technology do manual labor better than humans but it can also solve problems better, in some cases.
Preparations should be made to help retrain and place workers whose jobs are being eliminated -- especially since some of society's most economically vulnerable people and communities will be hit the hardest by the transition.
But while plenty of jobs will be automated out of existence, many types of jobs will remain resilient to automation. And, many of the people whose jobs are replaced by machines and algorithms will do what human beings have always done when technology has forced one of these transitions -- they find better and more interesting things to do with their time. Some of them will even invent new things and push humanity forward in the process.
That's not to belittle or demean people who worry about losing their jobs. There are few things more human than fearing for our jobs and the livelihood of our families. From the time humans stopped hunting-and-gathering and started settling in communities and taking on specialized roles in those communities, we've worried about our roles becoming useless and not being able to earn our keep.
That only intensified after the Industrial Revolution when factories and industry jobs replaced work that involved skilled trades, farming, and the labor to make handmade goods. More and more people became dependent on companies for the work to earn their livelihood.
So what happens when those companies replace a lot of those jobs with robots and algorithms? That's the question hanging over humanity. The answer is that humans usually find new things to do.
For example, farming used to be one of the largest labor sources in the United States. But, advancements in the way we farm have made it far more efficient and dramatically reduced the number of workers it takes to run farms -- from 10 million in 1950 to 3 million by 2010, according to the National Agricultural Statistics Service. During that same period, the U.S. technology industry was created and by 2014 it employed 6.5 million workers, according to CompTIA.
While those numbers net out quite nicely, obviously not all of those farmers became computer technicians and software engineers. But, it's probably fair to say that a share of the kids who might have worked on the family farm ended up getting educated in computers and ultimately found more lucrative work there.
It's the same principle that recessions tend to spawn surges of innovation. Many of today's leading tech companies -- including Apple, Google, Microsoft, and Facebook -- were all born during economic downturns. The Panic of 1873 was followed by a surge of new patent filings and the decades that followed gave us the light bulb, the telephone, the phonograph, the electrical grid, and the urban subway system.
Part of these outpourings is due to "necessity being the mother of invention" but part of it is also due to humans giving in to their natural curiosity and creativity when they have extra time on their hands. All of the things that robots and algorithms are good at mostly involve brute force -- physical or computational. They don't involve creativity or nuance, empathy or finesse.
Humans got to the top of the food chain and became the shapers of the planet because of the size of our brains. We're slower than a lot of other animals. Many of them are stronger than us. And we don't have many natural gifts to be good hunters. But we make great tools. And those tools allow us to move across the ground faster than cheetahs, to fly farther than hawks and eagles, and to produce food in such quantities that we can put ourselves to work on other tasks.
Those tools include AI and robotics. When we think about how robotics, AI, and automation will cause havoc to today's economic models, then the future does look bleak for workers. There's likely to be displacement, upheaval, and societal changes when these trends fully take hold. But, we also shouldn't discount that because of its potential scale, it will likely unleash an unprecedented new wave of innovation.
It will take a lot of people out of mindless jobs and give them the greatest resource of innovation: time.
Again, I don't want to downplay the deprivation and heartache that are often a feature of these transitions. But as we anticipate the massive effects that automation will bring, we should also remember that we won't know the full unintended consequences of untethering all of that human creativity and potential at once.
ZDNet: http://http://zd.net/1htvsUt


























